The present continuous tense
Join EnglishTopVN to immediately learn important knowledge about PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE with formulas, signs, and exercises with detailed answers. Besides, you need to practice the present continuous tense to consolidate your knowledge for all tests.
1. Concepts
Present Continuous used to describe events that happen right at the time we speak or around the time of speaking, and the action has not ended (still continuing).
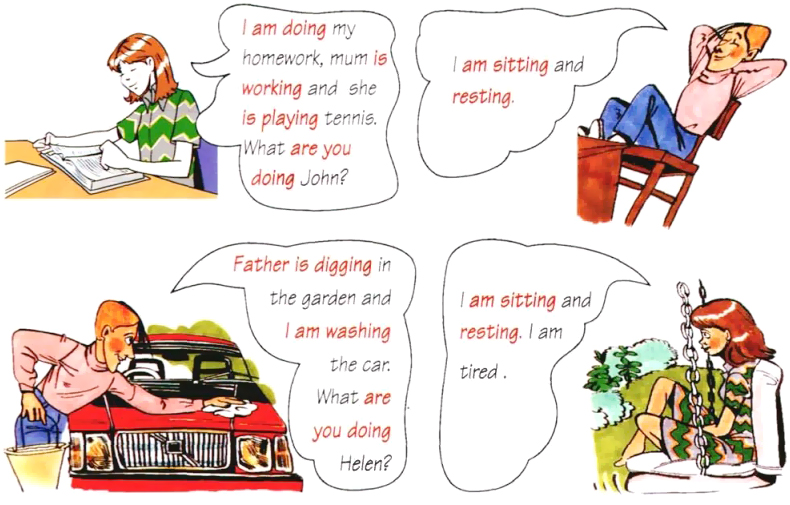
Example of present continuous tense
2. Formula
2.1. Affirmations
S + am/ is/ are + V-ing
✎ NOTE:
– S = I + am
– S = He/ She/ It + is
– S = We/ You/ They + are
We see that the verb in a sentence using the present continuous tense needs to have two components: the verb "tobe" and "V-ing". Depending on the subject, the verb "to be" has different conjugations.
For example:
a) They are watching TV now.(They are watching TV now.)
b) She is cooking with her mother. (She is cooking with her mother.)
c) We are studying English. (We are learning English.)
2.2. Negative sentence
S + am/ is/ are + not + V-ing
✎ NOTE:
– am not: there is no abbreviation
– is not = isn’t
– are not = aren’t
===> For negative sentences of the present continuous tense, we just need to add “not” after the verb “tobe” and then add the verb ending “–ing”.
For example:
a) I am not listening to music at the moment. (I'm not listening to music right now.)
b) My sister isn’t working now. (My sister is not working.)
c) They aren’t watching the TV at present. (They are not watching TV right now.)
2.3. Question
Am/ Is/ Are + S + V-ing ?
Reply:
- Yes, I am. – Yes, he/ she/ it + is. – Yes, we/ you/ they + are.
- No, I + am not. – No, he/ she/ it + isn’t. – No, we/ you/ they + aren’t.
===> For interrogative sentences, we just need to invert the verb “tobe” before the subject.
For example:
a) -Are you doing your homework? (Are you doing your homework?)
- Yes, I am./ No, I am not.
b) -Is he going out with you? (Is he going out with you right?)
- Yes, he is./ No, he isn’t.
c) Are they studying English?(Are they learning English?)
- Yes, they are./ No, they aren't.
3. How to use
➣ Describe an action happening at the moment of speaking
For example:
-
They are watching TV now. (They are watching TV now.)
-
Tim is riding his bike to school at the moment. (At this moment Tim is cycling to school.)

They are watching TV now
➣ Describes an event or action that is generally happening but not necessarily happening at the moment of speaking
For example:
-
Iam finding a job.(I am looking for a job.)=> It's not necessarily that I'm looking for a job at the time of speaking, but I'm in the process of looking for a job (after graduating or after leaving my old company.)
-
He is reading "Gone with the wind". (He is reading "Gone with the wind".) =>It means that she started reading this book a few days ago but hasn't finished it yet, but at the moment of speaking she is not reading this book.

He is reading "Gone with the wind"
➣ Describes an event that has been planned for the future
For example:
-
I bought the ticket yesterday. I am flying to New York tomorrow.(I bought the ticket yesterday. Tomorrow I will fly to New York.)
-
What are you doing next week? (What will you do next week?)

I bought the ticket yesterday. I am flying to New York tomorrow.
➣ Describes a frequently repeated action that causes annoyance or discomfort to the speaker, often used in sentences that use “always”
For example:
-
He is always coming late. late. (He is always late.)
-
Why are you always putting your dirty clothes on your bed? (Why do you always leave dirty clothes on the bed?)
-
They are always arguing. (They always argue with each other.)

They are always arguing
➣ Used to describe something that changes or develops
-
The children are growing Quickly. (The child grew tall so quickly.)
-
The climate is changing rapidly. rapidly. (The climate changes rapidly.)
-
Your English is improving. (Your English is improving.)

The children are growing quickly
➣ Describes something new, in contrast to a previous situation
-
These days most people are using email instead of written letters. (Today most people use email instead of writing letters by hand.)
-
What sort of clothes are teenagers wearing nowadays? What sort of music are they listening big? (What kind of fashionable clothes are the teenagers wearing? What kind of music are they listening to?)
These days most people are using email instead of writing letters
4. Identification signs
➣ In the sentence there are adverbs of time
– Now: now – Right now: Right now – At the moment: at this moment – At present: at present – At + specific time (at 10 o’clock)
For example:
-
I am not listening to radio at the moment. (I'm not listening to the radio right now)
-
It is storming now. (It's stormy)
➣ There are verbs in the sentence – Look! (Look!)– Listen! (Listen!)– Keep quiet! (Be quiet)
For example:
-
Now my sister is going shopping with my father. (Now my sister is going shopping with my dad.)
-
Look! The bus is coming. (Look! the bus is coming.)
-
Listen! Someone is laughing. (Listen! Someone is laughing.)

