Simple future tense
Join EnglishTopVN to immediately learn important knowledge about SIMPLE FUTURE tense with formulas, signs, and exercises with detailed answers. Besides, you need to practice the simple future tense to consolidate your knowledge for all tests.
1. Concepts
Simple future tense in English (Simple future tense) is used when there is no plan or decision to do anything before we speak. We make spontaneous decisions at the moment of speaking.

2. Formula
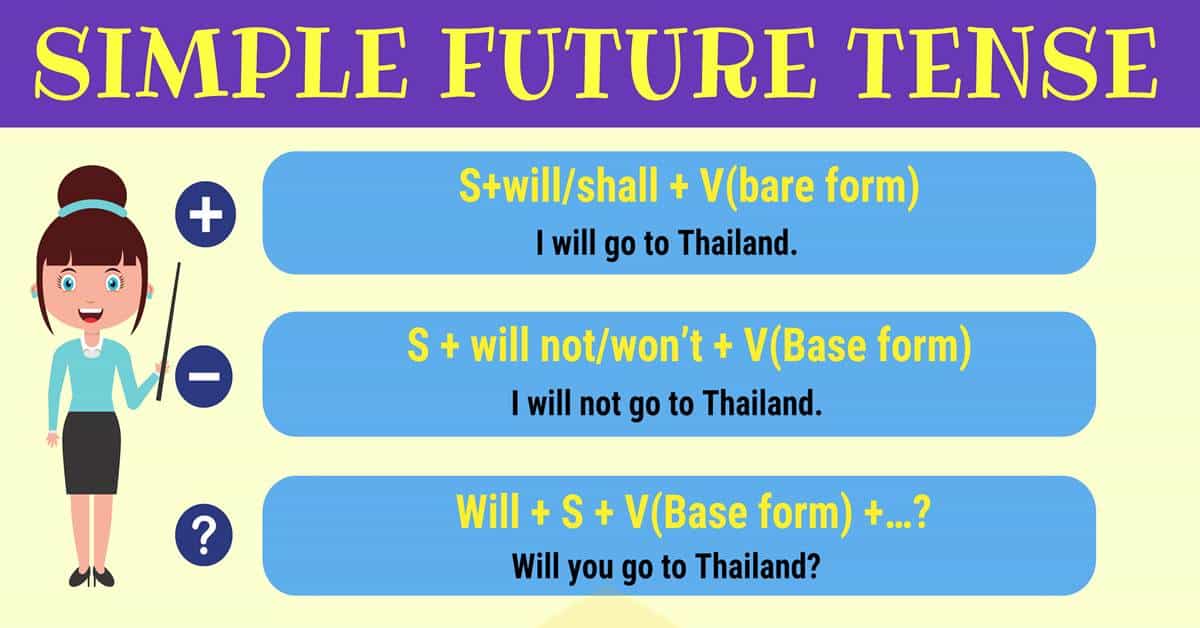
Simple future formula
2.1. Affirmations
|
Verb tobe |
Regular verbs |
|
|
Structure |
S + will + be + N/Adj |
S + will + V(infinitive) |
|
Note |
will = ‘ll |
|
|
For example |
- She‘ll be fine.(She will be fine.) - You will be mine soon(I will soon belong to you.) |
- I will always love you. (I will always love you.) - No worries, I will take care of the children for you. (Don't worry, I'll take care of the children for you.) |
2.2. Negative sentences
|
Verb tobe |
Regular verbs |
|
|
Structure |
S + will not + be + N/Adj |
S + will not + V(infinitive) |
|
Note |
will not = won’t |
|
|
For example |
– She won’t be happy if she cannot pass the entrance exam tomorrow. She won't be happy if she doesn't pass the entrance exam tomorrow. – We won’t be friends anymore. (We won't continue to be friends anymore.) |
– I won’t bring champagne to the party tonight.(I won't bring Champagne to the party tonight.) – I won’t tell her the truth.(I won't tell her the truth.) |
2.3. Question
|
Verb tobe |
Regular verbs |
|
|
Structure |
Q:Will + S + be + ? A:Yes, S + will No, S + won’t |
Q:Will + S + V(infinitive)? A:Yes, S + will. No, S + won’t. |
|
For example |
- Q: Will you be home tomorrow morning? (Are you at home tomorrow morning?) Yes, I A: No, I won’t (No, I won't be home) - Q: Will he be the last person to leave the classroom? (He will be the last to leave the classroom, right?) A: Yes, he will (Yes, he will stay) |
- Q: Will you come back? (Are you coming back?) A: Yes, I will (Yes, I'll be back) - Q: Will he go to the post office to take the parcel for you? (Will he come to the post office to pick up your parcel?) A: No, he won’t (No, he won't) |
3. How to use
3.1. Expresses a decision or a temporary intention that occurs at the time of speaking. There are signal words that indicate time in the future
For example:
- I miss my grandmother so much. I will drop by her house after working tomorrow
(I miss my grandmother very much so after work tomorrow I will visit her.)
3.2. Expresses an unfounded prediction
For example:
- I think she won’t come and join our party.
(I think she won't come to our party.)
3.3. Make requests, suggestions, invitations
For example:
- Will you go out for dinner with me? (Can you go to dinner with me?)
- Will you pass me the pencil, please? (Can you pass the pencil to me?)
3.4. Express a promise
For example:
- I promise I will write to her every day. (I promise I will write to her every day.)
- My friend will never tell anyone about this. (My friend won't tell anyone about this.)
3.5. Expresses a warning or threat
For example:
- Be quiet or Chinhtao will be angry. (Be quiet, otherwise Chinhtao will get angry.)
- Stop talking, or the teacher will send you out. (Don't talk anymore, otherwise the teacher will kick you out of class.)
3.6. Used to offer help to others
(1 guess question starting with Shall I)
For example:
- Shall I carry the bags for you, Dad? (Let me carry these bags for you, Dad.)
- Shall I get you something to eat? (I'll bring you something to eat, okay?)
3.7. Used to give some suggestions
Guessing questions begin with Shall we
For example:
- Shall we play football?
- Shall we have Chinese food? (Let's eat Chinese food.)
3.8. Used to ask for advice
What shall I do? hoặc What shall we do?
For example:
- I have a fever. What shall I do?
- We're lost. What shall we do? (We're lost. What should we do now?)
3.9. Used in conditional sentences type I, expressing an assumption that may happen in the present and future
For example:
- If she learns hard, she will pass the exam.
4. Identification signs
➢ Signs to recognize the simple future are very simple. You just need to pay attention to the examples of simple future tense to be able to recognize it.
4.1. Adverbs of Time
- Print + (time): for how long (in 5 minutes: for 5 minutes)
- Tomorrow: tomorrow
- Next day/ next week/ next month/ next year: next day, next week, next month, next year.
- Soon: soon
For example:
- We'll meet at school tomorrow. (Tomorrow we will meet at school.)
4.2. There are verbs in the sentence that indicate opinion
- Think/ believe/ suppose/ assume…: think/ believe/ assume
- Promise: promise
- Hope, expect: hope/expect
For example:
- I hope I will live abroad in the future. (I hope to live abroad in the future.)
4.3.In the sentence there are adverbs that show opinion
- Perhaps/ probably/ maybe: có lẽ
- Supposedly: supposedly, suppose
For example:
- This picture is supposedly worth a million pounds.
(This painting is said to be worth a million pounds)
5. Some structures have futuristic meanings
We can use a number of other grammatical structures that have similar functions to the simple future tense, expressing actions and events that are likely to happen in the future such as:
| (to be) likely to + V (possible/can) |
I believe that technological innovations such as robotsare likely todo most of human’s workin the future. |
| (to be) expected to + V
(expected) |
Artificial intelligenceis expected toreplacehuman in most manual work in the near future. |
6. The difference between the two tenses
The difference between the simple future tense and the structure ‘be going to + V’
The biggest difference between the simple future tense and the structure 'be going to + V' lies in the possibility of the speaker's judgment and prediction. So:
- Use the form ‘be going to + V’ if there is evidence to support your judgment.
- Use the future simple or alternative structures if your judgment is based only on feelings and without evidence or clear grounds.

