Past Perfect Tense
Join EnglishTopVN to immediately learn important knowledge about PAST PERFECT tense with formulas, signs, and exercises with detailed answers. Besides, you should practice the past perfect tense to consolidate your knowledge for all tests.
1. Concepts
past perfect tense used to describe an action that happened before another action and both of which happened in the past. Actions that happen first use the past perfect tense, actions that happen later use the past simple.

Examples of past perfect tense
2. Formula

2.1. Affirmations
S + had + past participle
For example:
- My brother had done his homework before I arrived.
- She had gone out when he came into the house.

2.2. Negative sentence
S + hadn’t + past participle
Where hadn't = had not
For example:
- He hadn't finished his breakfast when I saw him.
- He hadn't come home when I got there.
2.3. Question
Question word + had + S + past participle
➣ How to answer:
Yes, S + had.
No, S + hadn’t.
For example:
- What had he thought before she asked the question?.
- Had the movie ended when he arrived at the cinema?
3. How to use
➨ To know when to use the past perfect; You need to clearly understand cases and situations so as not to confuse the past perfect and past simple.
3.1. Expresses an activity that happened and was completed before another action in the past
For example:
- Jane had cooked breakfast when we got up.
- The plane had left by the time I arrived at the airpot.
3.2. Describes an action that happened and lasted up to a certain time in the past
For example:
- We had that car for ten years before it broke down.
- By the time Alex finished his studies, he had been in London for over eight years.
3.3. Describes an action that happened before a certain time in the past
For example:
- She had travelled around the world before 2010.
- He had never played football until last week.
3.4. Describes an action that occurs as a first condition for another action
For example:
- Tom had prepared for the exams and was ready to do well.
- Dunny had lost twenty pounds and could begin anew.
3.5. Used in type 3 conditional sentences to express unreal conditions in the past.
For example:
- If I had known that, I would have acted differently.
- She would have come to the party if she had been invited.
3.6. Used to express disappointment about something in the past
These uses are often found in past tense constructions.
For example:
- We wished we had purchased the ticket.
- I wished I had told the truth.
4. Identification signs
Signs of the past perfect are often conjunctions.
4.1. Recognition words
- Until then, by the time, prior to that time, before, after, for, as soon as, by, …
- Before, after, when by, by the time, by the end of + time in the past …
For example:
- Before I went to school, my mother had packed me a lunch.
- By the timethey broke up, they had lived with each other for 3 years.
- He hadn’t recognized it until i told him.
4.2. Position of conjunctions
4.2.1. When
For example:
-
When they arrived at the airport, her flight had taken off before 2 hours.
4.2.2. Before
Before “before” use the past perfect tense and after “before” use the simple past tense.
For example:
-
He had done his homework before his mother asked him to do so.
4.2.3. After
Before “after” use the simple past tense and after “after” use the past perfect tense.
For example:
-
They went home after they had eaten a big roasted chicken.
4.2.4. By the time
For example:
-
He had cleaned the house by the time her mother came back.
4.2.5. No sooner… than…
This is an inversion structure that only uses the past perfect tense. Recipe:
Whatever subject 1 has just done, subject 2 will do something else immediately.
For example:
-
No sooner had Linda closed this door than her friend knocked.
-
No sooner had we opened the shop than ten customers came into.
4.2.6. Hardly/Barely/Scarcely … when …
This is an inversion structure that only uses the past perfect tense. This structure is synonymous with the structure No sooner… than… Recipe:
Barely/Hardly/Scarcely + had + Subject 1 + Verb 1 (V3/V-ed) + when + Subject 2 + Verb 2 (V2/V-ed)
Whatever subject 1 does, subject 2 does something else immediately.
Note: Subject 1 and subject 2 can be the same or different.
For example:
-
Hardly had we gone out when it rained.
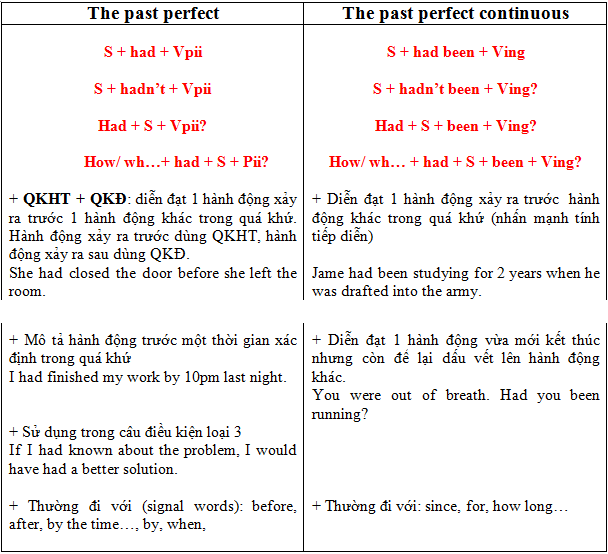
5. Distinguish between past perfect and past perfect continuous
➨ The distinction between the two Past Perfect Tense and past perfect continuous tense in English causes many difficulties for many people. Below is a comparison table of these two tenses.