Overview of nouns
EnglishTopVN introduces details about nouns such as definition of nouns, singular and plural nouns, the role of nouns in sentences, types of nouns, how to change from singular nouns to plural nouns and how to use them. Use the genitive with nouns.
➢ Nouns in English can be classified into the following categories:
Singular Nouns & Plural Nouns
Countable Nouns & Uncountable Nouns
➢ So what are the differences between these types and how do they affect the grammar of a sentence? Let's find out below!
1. Singular and plural nouns
✅ Summary:
➢ Unlike Vietnamese, nouns in English have two different forms: singular and plural.
➢ If we talk about quantities of 2 or more, we must use plural nouns.
Cases of plural nouns:
- Common: Add -s or -es to singular nouns
- Some nouns have irregular plural forms
- Some nouns have the same plural form as their singular form
1.1. Concept
➢ In Vietnamese, nouns never change in number:
He has one apple.
I have two apple.
=> The noun "apple" is always "apple", whether the quantity is 1 apple or 2 apples.
➢ English, on the other hand, makes a distinction between singular numbers and plural numbers:
+ If the quantity is 1 then we obligatory must use noun in singular form:
- He has an apple.
+ If the quantity is 2 or more then we obligatory must use noun in plural form:
- He has two apples.
➢ However, for most nouns in English, the singular and plural forms are quite similar. Most plural forms can be easily deduced from the singular form, for example:
- pen → pens
- cat → cats
- tomato → tomatoes
1.2. Rules for converting singular nouns into plural nouns
Case 1: Add -s or -es into singular nouns
For most nouns in English, we simply add the ending -s or -es After a singular noun, there will be a plural noun.
➢ So when to add -s, when to add -es? Let's look at the following summary of cases:
| Singular noun | Plural noun |
|---|---|
| Most nouns | More-s:
|
| Most nouns end in -ch, -s, -sh, -x, -z |
More-es:
However, if the word -ch pronounced /k/ then add-s:
Some plural cases do not add-es:
|
| Nouns ending in letters -y |
If before -y is a consonant, changing letters -y wall -i, then add -es:
If before -y is a vowel, add -s Normal:
|
| Nouns ending in letter -o |
Most nouns end in -o all add -s:
A few add more -es:
|
| Most nouns end in letters -f or -fe |
Change letters -f wall -v then add -es:
Some exceptions:
|
Case 2: The plural form changes irregularly
➢ There are some nouns in English that do not form their plural by adding -s or -es.
It may sound a bit complicated, but because these are common nouns, you will see them over and over again, and soon you will remember these special plural nouns !
➢ Here are some common nouns:
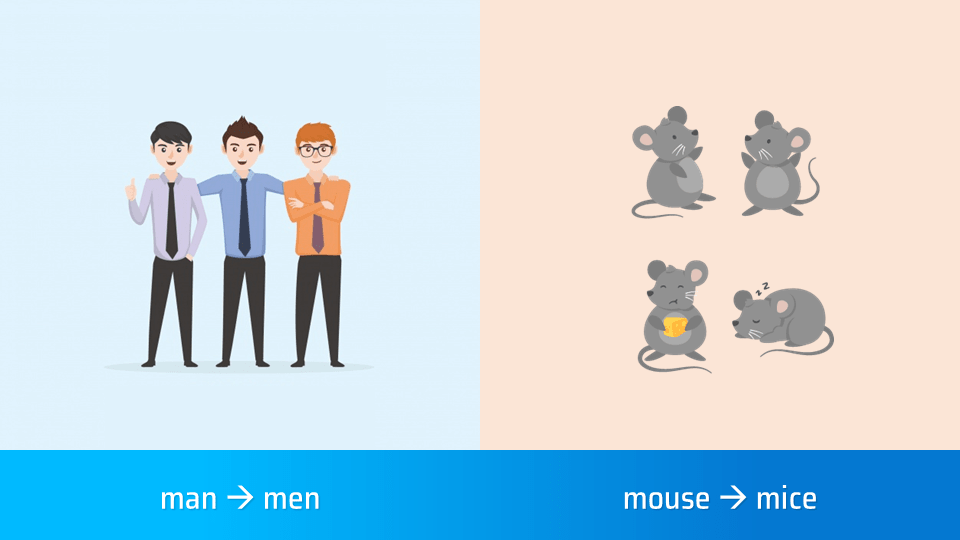
- man → men
- woman → women
- child → children
- person → people
- foot → feet
- tooth → teeth
- mouse → mice
➢ In addition, English words originating from other languages can have two plural forms: the added form -s/-es and the plural form borrowed from the original language:
- antenna → antennae or antennas
- cactus → cacti or cactuses
- formula → formulae or formulas
- millennium → millennia or millenniums
➢ We can remember these nouns no matter how much we learn them. There is no need to learn all such nouns at once, because it will be difficult to remember and very confusing!
Case 3: The plural form does not change compared to the singular form
➢ Besides, there are some nouns that have identical singular and plural forms. Interestingly enough, these words are often nouns referring to animals:
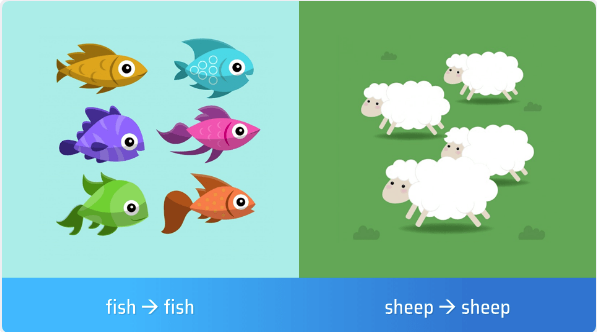
- fish → fish
- quail → quail
- sheep → sheep
- shrimp → shrimp
In addition, there are also some other words that fall into this case:
- means → means
- series → series
- species → species
2. Grammar related to singular and plural nouns
➢ Singular Nouns & Plural Nouns affect grammar in two ways:
- If the noun has a quantity of 2 things or 2 people or more, we are required to use the plural form.
- Among determiners, some words can only go with singular nouns, some can only go with plural nouns, some words can go with both.
- If the noun acts as the subject, the verb will have to change depending on whether the noun is singular or plural.
➢ The last point is extremely important in English grammar. Below is a table summarizing how to conjugate verbs according to singular and plural nouns:
| Singular verb | Plural verbs | |
|---|---|---|
| Verb to be in present tenses | is | are |
| Verb to be in past tenses | was | were |
| Verb to have in present tenses | has | have |
| Verbs often differ in present tenses | (add -s or -es) For example: works, washes |
(prototype) For example: work, wash |
| Modal verbs (like will, can, may,...) | (prototype) For example: will, can, may |
(prototype) For example: will, can, may |
3. Some special cases
✅ Summary:
➢ There are some special cases to note to avoid confusion:
- There are nouns that only have a plural form, not a singular form
- There are nouns that end in -s but are singular nouns
Special case 1: Nouns that only have a plural form, not a singular form
➢ In English there are some nouns that only have a plural form and no singular form, because they are often things that have two similar parts.
Here are some typical examples:
- Clothes:
- jeans
- pajamas
- pants
- shorts
- Tool:
- binoculars
- headphones
- glasses
- scissors

➢ In addition, we also have some other nouns that only have plural forms such as:
- belongings
- clothes
- congratulations
- earnings
- goods
- savings
- stairs
- surroundings
- thanks
Special case 2: Nouns that end in -s but are singular nouns
➢ Avoid confusing the following nouns as plural. Here are some typical examples:
- news
- mathematics
- physics
- aerobics
- gymnastics
- politics

4. Countable and uncountable nouns
✅ Summary:
Uncountable nouns are nouns that cannot be counted in quantities of 1, 2, or 3 but can only be measured through another unit.
For example:
water = water (uncountable noun)
a glass of water = a glass of water (measured through the unit of a glass)
5. Grammatical characteristics of uncountable nouns
➢ Uncountable nouns have the following grammatical features:
- Uncountable nouns have no singular or plural form, only one form.
- Among determiners, only some words can go with uncountable nouns.
- If an uncountable noun is the subject, the verb will be singular.
|
Singular verb |
|
|---|---|
|
Verb to be in present tenses |
is |
|
Verb to be in past tenses |
was |
|
Verb to have in present tenses |
has |
|
Verbs often differ in present tenses |
(add -s or -es) For example: works, washes |
|
Modal verbs (eg will, can, may,...) |
(prototype) Examples: will, can, may |

